What is the basic structure of a gate valve?
Introduction
As an important type of valve, gate valves are widely used in various fluid pipeline systems. Their internal structures can be classified into multiple types based on different classification criteria. The following will detail the classification of the internal structure of gate valves and their working principles.
The basic structure of a gate valve
A gate valve is mainly composed of a valve stem, valve body, bonnet, gate, actuator, and other parts (such as fasteners, valve stem nuts, packing, etc.). These components work together to achieve the opening and closing functions of the gate valve.
Classification by gate type
Wedge gate
– Single wedge gate: The sealing surface of the wedge gate forms a certain angle with the vertical centerline of the gate, suitable for high-pressure gate valves. It has good sealing performance, but the structure is relatively complex, and the sealing performance may be affected at high temperatures.
– Elastic gate: The elastic gate achieves sealing through elastic elements, suitable for medium and small diameters, various pressures and temperatures of gate valves, especially for media with fewer solid particles.
– Double gate: The double gate is composed of two gates and is hinged together to form a wedge gate. Its advantage is that it has lower requirements for the accuracy of the sealing surface angle and is less likely to get stuck due to temperature changes.
Parallel gate
– Single parallel gate: Simple structure and easy to process, but relatively poor sealing performance. It is suitable for medium and low pressure and medium and large diameter pipelines, and is often used in oil, gas, and natural gas pipelines.
– Double parallel gate: It is divided into self-sealing type and spread type. The self-sealing type achieves sealing by the pressure of the medium, while the spread type uses the top wedge to make the two gates move horizontally in opposite directions to achieve sealing.
Classification by valve stem support type
Rising stem gate valve
– In this structure, the handwheel or other actuator is fixed on the valve stem nut. When the handwheel rotates, the valve stem nut rotates, driving the valve stem to move up and down, thereby controlling the movement of the gate. When the rising stem gate valve is open, the valve stem extends above the handwheel, directly indicating the opening degree of the gate valve, which is convenient for operation. However, due to the exposed threads, it is prone to dust accumulation in the air, accelerating thread wear, so it should be installed indoors as much as possible.
Non-rising stem gate valve
– The handwheel of the non-rising stem gate valve is fixed on the valve stem, and the valve stem thread is fixed on the top of the gate. When the handwheel rotates, the valve stem thread drives the gate to move up and down, while the valve stem itself only rotates and does not rise. This structure requires less installation space and is suitable for large channel gate valves or where installation space is limited. However, since the valve stem does not rise, the opening degree cannot be directly indicated by the length of the valve stem extension, so an opening indicator needs to be installed.
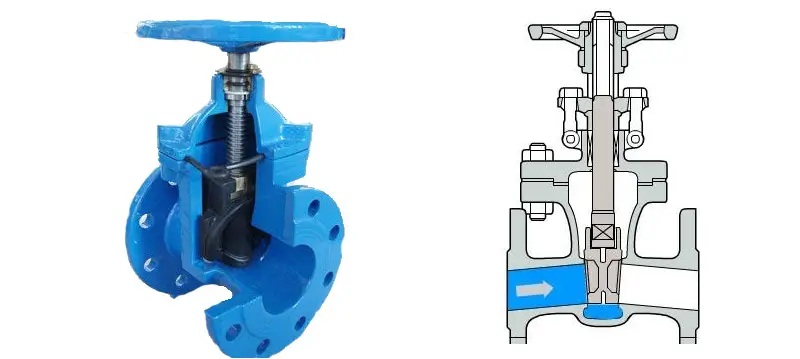
The working principle of a gate valve
The gate of a gate valve moves in a straight line along with the valve stem. Usually, there are trapezoidal threads on the lifting rod, which, through the nut at the top of the valve and the guide slot on the valve body, convert rotational motion into linear motion, that is, transform the operating torque into operating thrust.
Application of gate valve
- Oil and gas transmission pipelines.
- Conveying pipelines and storage equipment for refined oil.
- Oil and natural gas exploitation wellhead device.
- City gas transmission pipelines.
- Tap water and sewage treatment projects.
Sealing technology of gate valves
Soft seal gate valves and hard seal gate valves are common devices for regulating flow interception. It has good sealing properties and a wide range of applications.
A soft-seal valve is a metal material on both sides of the sealing pair and an elastic non-metallic material on the other side. This kind of seal has good sealing performance, but it is not resistant to high temperature, easy to wear, and has poor mechanical properties. A hard seal valve is a valve that is made of metal or other hard materials on both sides of the sealing pair, which is called a “hard seal”. This kind of seal has poor sealing performance, but it has high temperature resistance, wear resistance, and good mechanical properties. The valve soft seal seat is made of non-metallic materials with certain strength, hardness and temperature resistance, with good sealing performance and zero leakage, but the life and adaptability to temperature are relatively poor. The hard seal of the valve is made of metal, and the sealing performance is relatively poor. Soft sealing can not meet the process requirements for some corrosive materials, and hard sealing can solve it. These two seals can complement each other, and the soft seal is relatively good in terms of tightness, but now the tightness of the hard seal of the valve can also meet the corresponding requirements.
