Valves are vital components in controlling fluid flow, from water in homes to oil and gas in industrial settings. The way valves connect to piping systems is crucial for safe and efficient operation. Here’s a brief overview of some common valve connection types:
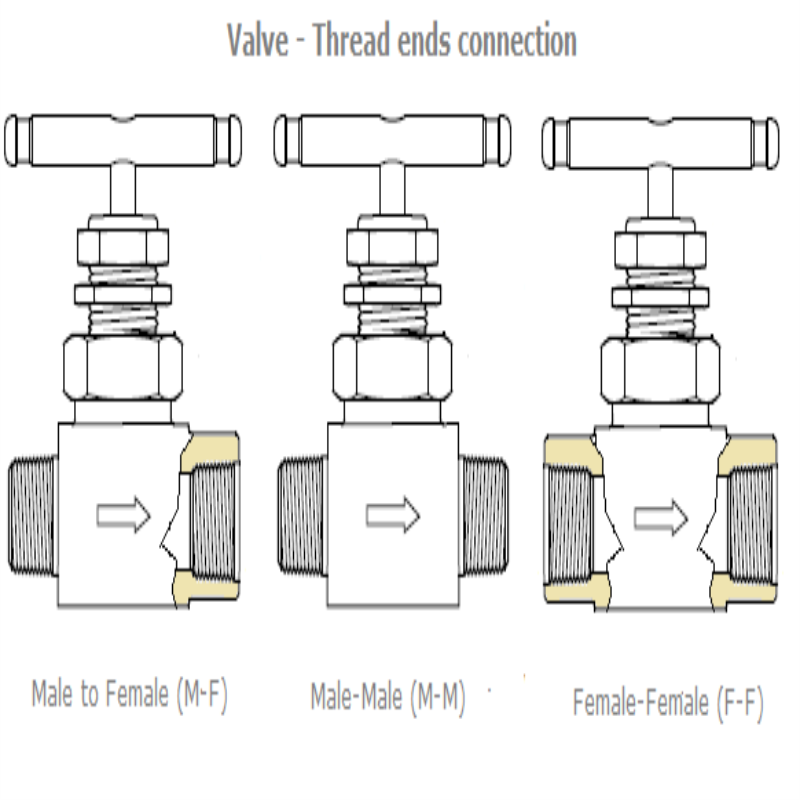
1. Threaded Connections
Threaded, or screwed, connections are simple and popular. They involve male and female threads that screw together, creating a seal. These valves are easy to install and remove, making them suitable for smaller systems or applications requiring frequent access. However, they may not hold up well under high pressure or temperature.
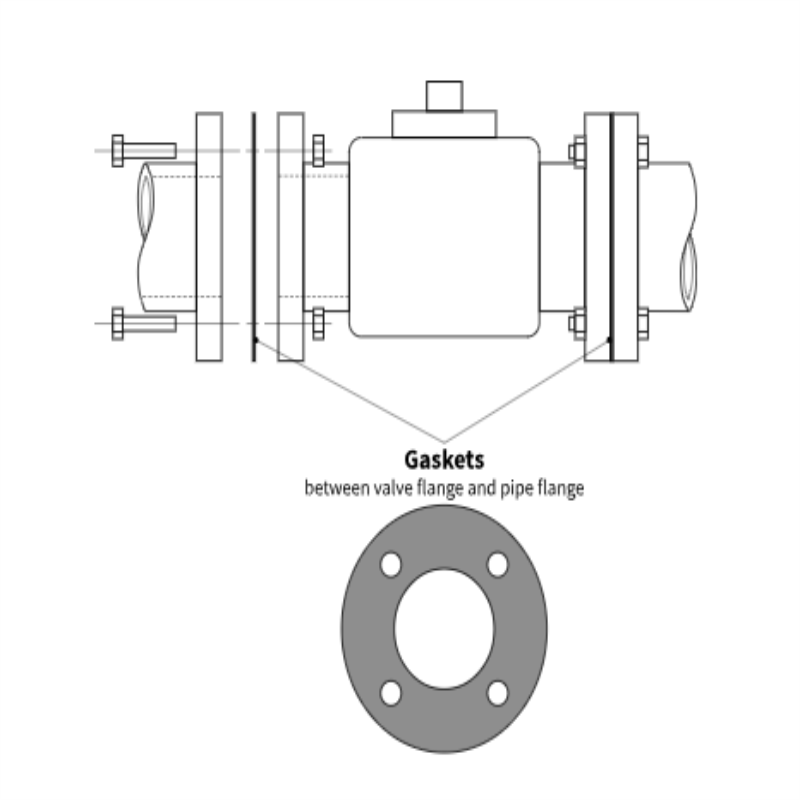
2. Flanged Connections
Flanged connections use flanges bolted together with a gasket in between to create a seal. They are sturdy and can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them ideal for large-scale piping systems. While installation takes more time and precision, flanged valves offer great versatility and are easily replaceable.
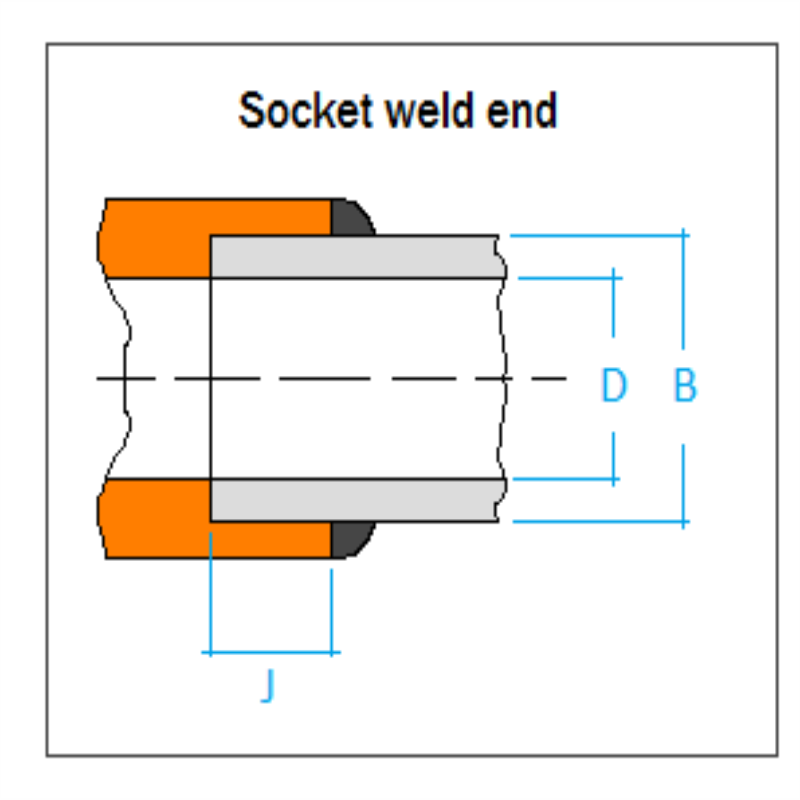
3. Socket Weld Connections
Socket weld connections involve welding the valve end into a socket welded onto the pipe. This creates a strong, leak-proof joint suitable for high-pressure applications. However, disassembly can be challenging, making socket weld valves less suitable for systems requiring frequent access.
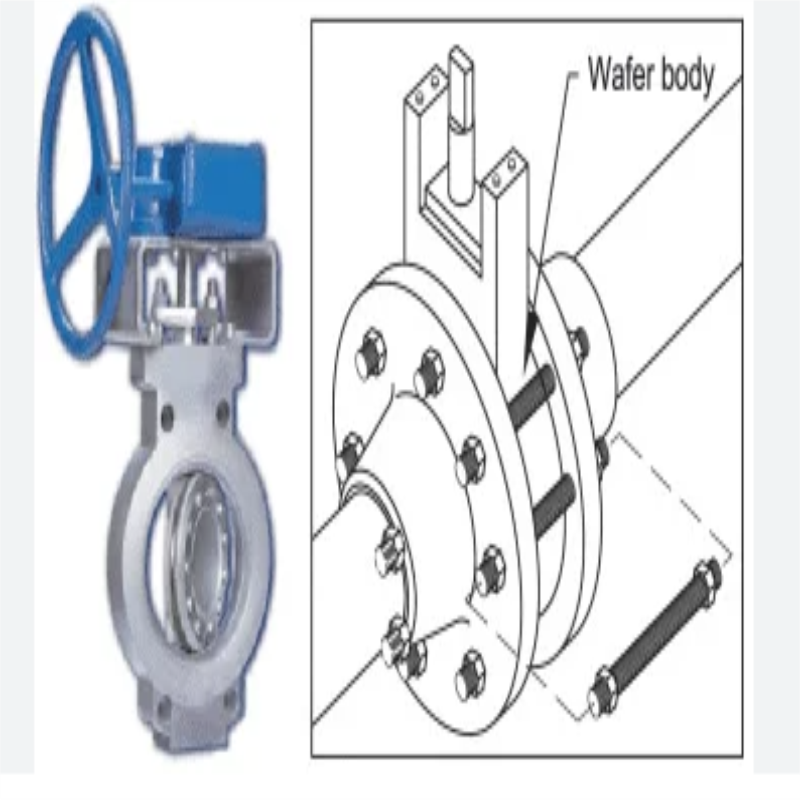
4. Wafer Connections
In a wafer connection the valve is installed between the pipe flanges and tightened to its place with the bolts for the pipe flanges. In some wafer types there are some centering holes on the body to ensure valve’s correct position between the flanges.
Wafer type body is the lightest body version for mounting between piping flanges. Therefore a wafer valve use to be cheaper than other valves. Also it is fast mounting.
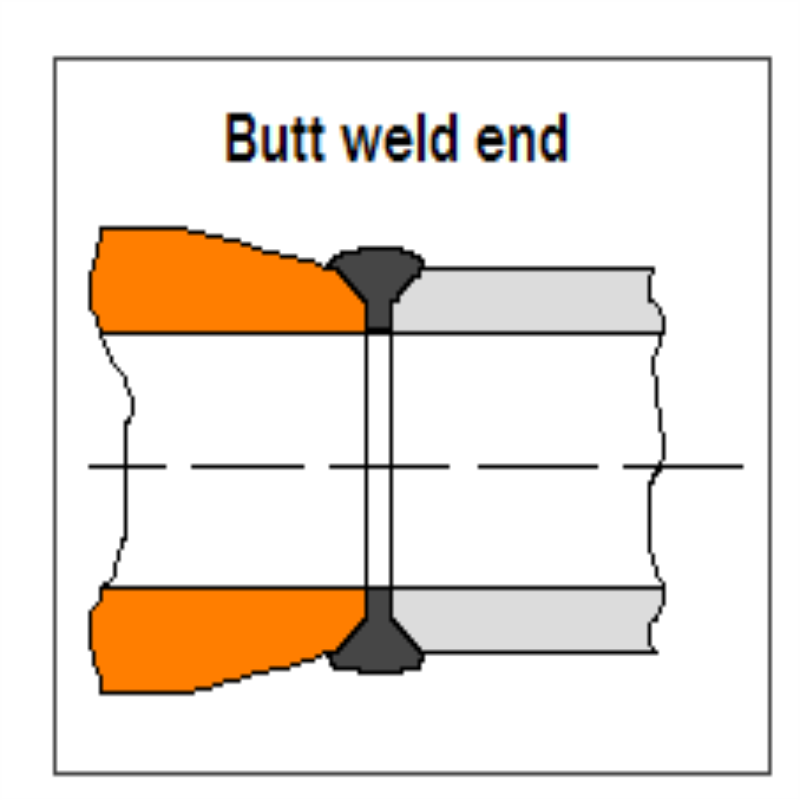
5. Butt Weld Connections
Butt weld connections involve welding the valve directly to the pipe, providing the strongest possible joint. They are ideal for extreme conditions like high pressure, high temperature, or corrosive environments. However, installation requires specialized welding techniques and careful preparation.
In conclusion, choosing the right valve connection type depends on your specific application’s requirements. Threaded connections are simple and convenient, while flanged and butt weld connections offer strength and durability. Socket weld connections strike a balance between strength and accessibility, while compression fittings are perfect for quick, easy installations. Understanding these options will help you select the best valve for your needs.
